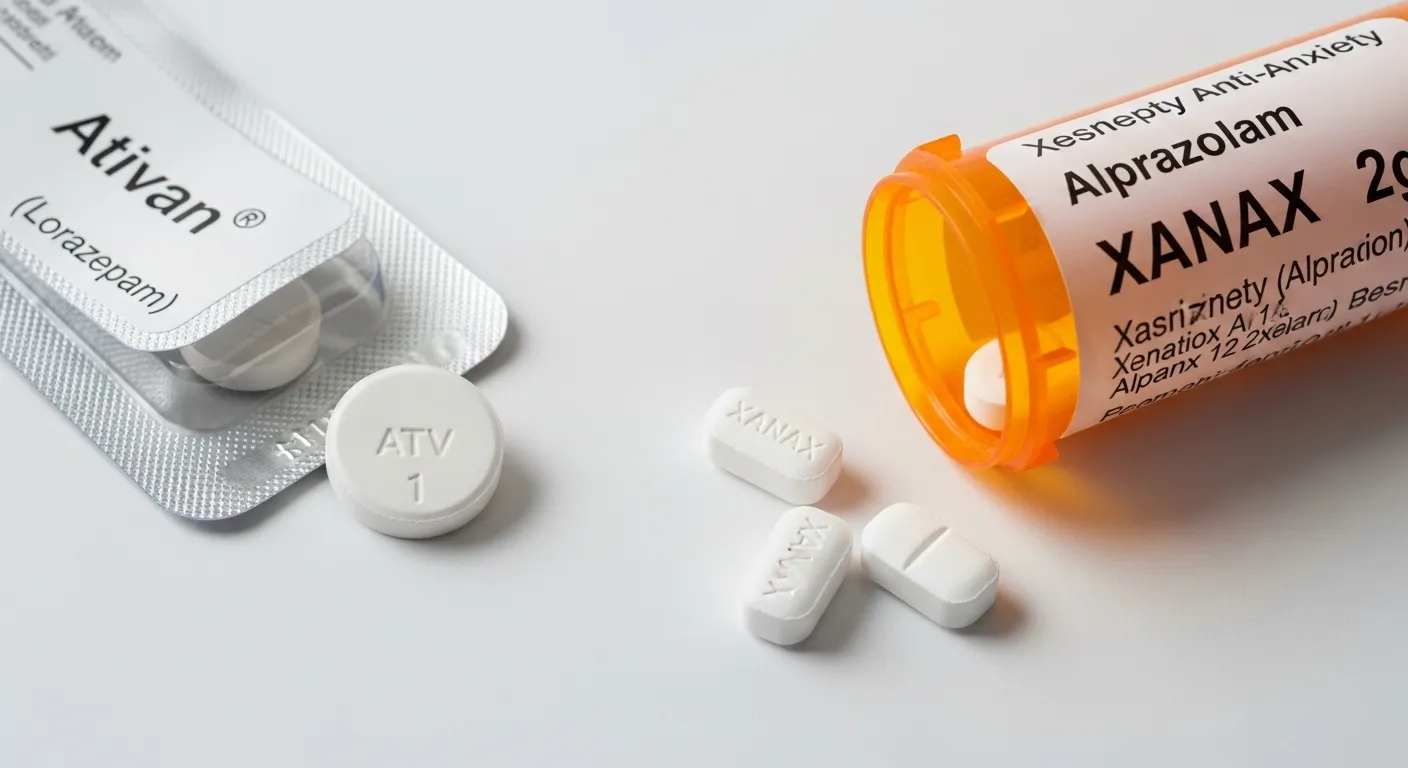
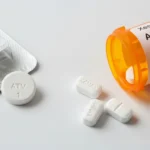
Many people feel confused when deciding between Ativan or Xanax. Both medications belong to a class called benzodiazepines, used to reduce anxiety, panic attacks, and insomnia.
If you’ve ever wondered which one is stronger, faster-acting, or safer, you’re not alone. Millions of searches every month try to answer the same question.
This guide will explain the differences, similarities, and correct usage of Ativan and Xanax. It will also provide practical examples, spelling insights, and professional advice to help you make informed decisions.
By the end, you’ll clearly understand Ativan vs Xanax, common mistakes people make, and which option might suit your needs best.
Ativan or Xanax – Quick Answer
Ativan (generic name: lorazepam) and Xanax (generic name: alprazolam) are both prescription medications for anxiety and panic disorders. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | Ativan (Lorazepam) | Xanax (Alprazolam) |
| Onset Speed | 30–60 minutes | 15–30 minutes |
| Duration | 6–8 hours | 4–6 hours |
| Common Uses | Anxiety, insomnia | Anxiety, panic attacks |
| Sedative Effect | Moderate | Stronger |
| Prescription | Daily or as needed | Daily or as needed |
Example: If someone experiences sudden panic attacks, Xanax may provide quicker relief. Ativan is often preferred for longer-lasting anxiety control.
The Origin of Ativan or Xanax
The confusion between Ativan or Xanax partly comes from their different origins.
- Ativan was first developed in the 1970s and became widely available in the 1980s. Its main purpose was long-term anxiety management.
- Xanax was introduced later, in the 1980s, and gained popularity for rapid relief of acute panic symptoms.
Both drugs belong to the same benzodiazepine family but differ in chemical structure and speed of action.
Why the confusion exists: Many people mix them up because they treat similar conditions. Additionally, their brand names are more commonly used than generic names, making searches like “Ativan or Xanax” common online.
British English vs American English Spelling
Interestingly, the brand names Ativan and Xanax are spelled the same in both British and American English. The confusion is not in spelling but in usage and pronunciation.
| Aspect | American English | British English |
| Brand Name | Ativan, Xanax | Ativan, Xanax |
| Common Usage | Anxiety, panic | Anxiety, panic |
| Prescription Notes | Written in mg | Written in mg |
| Generic Recognition | Lorazepam, Alprazolam | Lorazepam, Alprazolam |
Tip: Unlike words like “color/colour” or “theater/theatre,” the spelling is identical globally, but doctors’ prescribing habits may vary.
Which Spelling Should You Use?
Since Ativan or Xanax doesn’t have spelling variations, your focus should be regional availability and prescription rules:
- United States: Both medications are widely prescribed. Insurance coverage and pharmacy availability may differ.
- United Kingdom & Commonwealth Countries: Available but often stricter prescription rules. Generic names (lorazepam/alprazolam) are preferred.
- Global Users: Always follow local medical guidelines. Brand names are recognized internationally, but dosage and brand popularity vary.
- Read Also.Waive or Wave: Which One Is Correct and When to Use Each?
Common Mistakes with Ativan or Xanax
- Mixing doses: People often confuse mg dosages; Xanax 0.5mg ≠ Ativan 0.5mg in strength.
- Assuming one is safer: Both drugs have similar side effects; misuse can cause dependence.
- Using without prescription: Dangerous and illegal in many countries.
- Confusing short vs long duration: Xanax works faster but lasts shorter; Ativan lasts longer but slower.
- Incorrectly switching brands: Never swap without consulting a doctor; generic versions may differ in absorption.
Ativan or Xanax in Everyday Examples
Here’s how the terms might appear in real-life communication:
- Email: “My doctor prescribed Ativan for my anxiety, but I’ve also heard Xanax is faster.”
- News Article: “Prescription rates of Ativan and Xanax have increased among young adults in the US.”
- Social Media: “Feeling anxious? Some people swear by Xanax, others prefer Ativan.”
- Formal Writing: “Lorazepam (Ativan) and alprazolam (Xanax) are effective benzodiazepines for managing acute anxiety.”
Ativan or Xanax – Google Trends & Usage Data
According to Google Trends:
- United States: Xanax is searched slightly more frequently than Ativan, especially around exam seasons or stressful periods.
- United Kingdom & Canada: Ativan searches are more common among adults aged 30–50.
- Global: Interest peaks often align with mental health awareness campaigns and seasonal stress periods.
This indicates that people search for “Ativan or Xanax” to understand which works better for their situation.
Keyword Comparison Table
| Feature | Ativan (Lorazepam) | Xanax (Alprazolam) |
| Onset Time | 30–60 minutes | 15–30 minutes |
| Duration | 6–8 hours | 4–6 hours |
| Anxiety Relief | Moderate, steady | Quick, strong |
| Dependence Risk | Moderate | High if misused |
| Typical Prescription | Daily or PRN | Daily or PRN |
FAQs
1. Can I take Ativan and Xanax together?
It’s not recommended. Combining them increases sedation and dependence risk. Always consult a doctor.
2. Which is stronger, Ativan or Xanax?
Xanax acts faster and may feel stronger initially. Ativan lasts longer for sustained relief.
3. Can I use them for sleep?
Both can cause drowsiness, but Ativan is preferred for longer sleep support.
4. Are there side effects?
Yes, both can cause drowsiness, dizziness, memory issues, and potential dependence.
5. Is one safer than the other?
Safety depends on dose, duration, and personal health. Follow medical advice.
6. How long does it take for Ativan to leave the system?
Typically 24–48 hours. Xanax is cleared faster, around 11 hours.
7. Can I switch from Xanax to Ativan?
Yes, but only under medical supervision to prevent withdrawal or overdose.
Conclusion
Choosing between Ativan or Xanax depends on your specific needs: fast-acting relief or longer-lasting anxiety control. Both are effective benzodiazepines, but misuse can cause dependence and health risks. Remember, spelling is the same worldwide, so focus on dosage, prescription rules, and personal health requirements.
Always consult a licensed doctor before starting, switching, or stopping any medication. Understanding the differences, correct usage, and common mistakes ensures safer and more effective treatment.
With proper guidance, Ativan or Xanax can help manage anxiety, improve sleep, and enhance daily life without confusion or risk.

Jon McGregor a British writer known for quiet, realistic stories. His writing focuses on everyday life and human emotions.